Endpoint security used to be simple: put strong passwords on computers, a firewall on the router, and keep the antivirus up to date. Once the endpoints were secure, the whole network was safe. These days, endpoint security, which includes printer security, is a bit more complex – making it even more necessary.
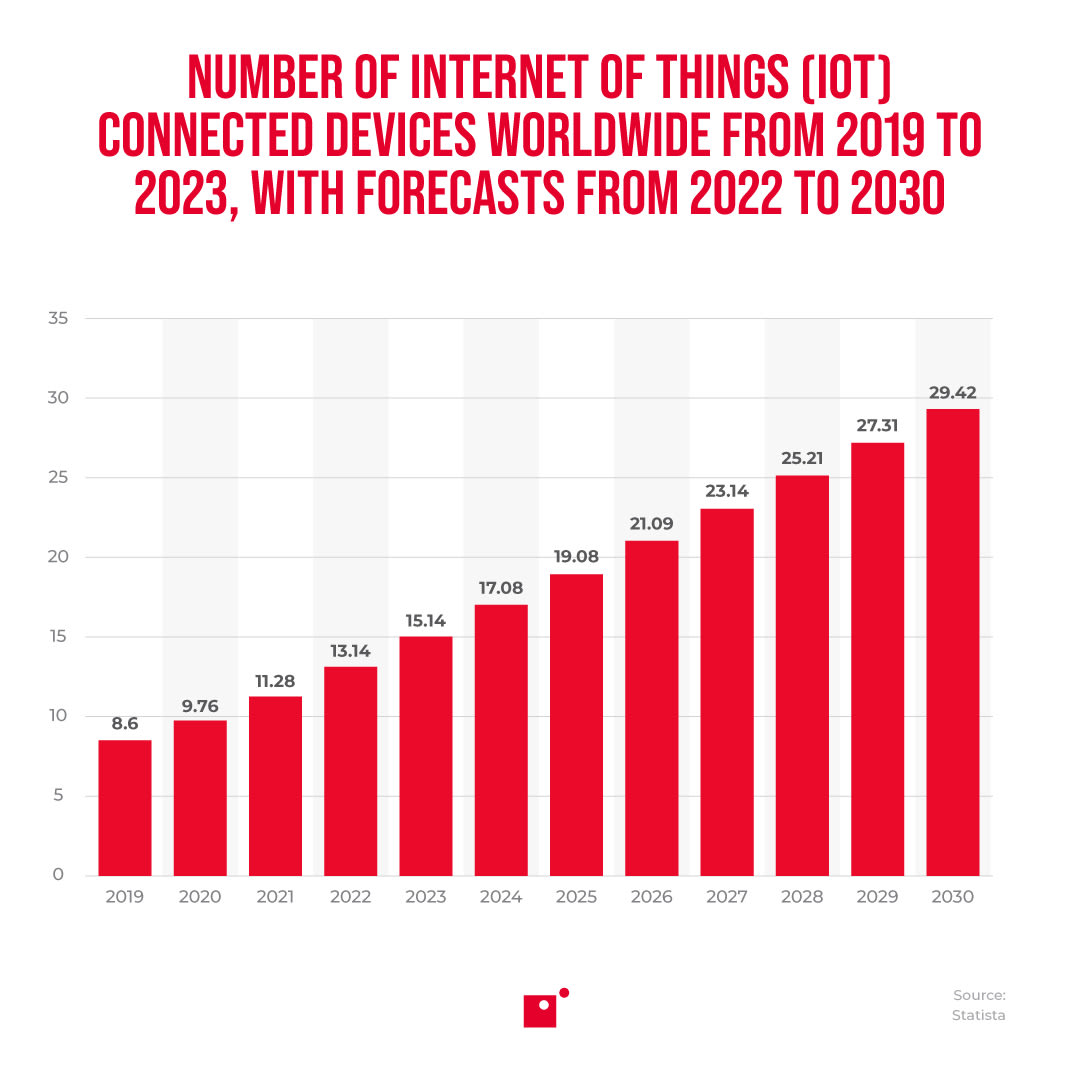
The role of endpoint security will only continue to grow in importance as the internet of things (IoT) continues to expand to record volumes year after year. As the large majority of modern printers are network enabled, they fall under the growing IoT umbrella, and if left unsecured, act as a major network vulnerability that threat actors can exploit.
If you’re interested in learning more about technology, how modern organizations overcome challenges, and expanding role of security in business strategy, subscribe to the Impact blog!
Printer Security: A Brief Overview
It can be easy to forget about printers when addressing endpoint security. But, if left neglected, this innocent office equipment quickly becomes a glaring vulnerability. The below video details some of the issues that can emerge if printers are left unsecured.
Because printers still handle highly sensitive documents, they need robust security measures put in place to ensure that data, documents, and operations remain protected from unauthorized access.
Keep in mind, printers aren’t the only network-enabled devices that need endpoint security provisions. With the astronomical volume of IoT devices worldwide, endpoint security is a vital consideration for any of the smart devices that live on your network.
The Place of the Printer in a Security Strategy
Modern printers store sensitive data in their internal memory, handle large volumes of confidential documents, but often lack robust security measures by default. If not properly secured, they can easily become an entry point for cybercriminals to infiltrate the broader network, leading to data breaches, intellectual property theft, and compliance violations.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must integrate printers into their cybersecurity protocols. This involves implementing strong authentication mechanisms to control access, encrypting data transmissions, regularly updating firmware, and performing routine security audits.
Additionally, organizations should establish clear policies for managing and disposing of print-related data to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. By treating printers as integral components of the network and incorporating them into the cybersecurity strategy, organizations significantly reduce any potential vulnerabilities and enhance their overall cybersecurity.
Common Printer Security Threats
The video at the top of this blog touched on a few of the common cyberattacks that threat actors launch against vulnerable printers, which are covered in further detail below and include:
- Document theft
- Cryptojacking
- Email attacks
- Traditional hacking
- Machine tampering
Document & Data Theft
Document and data theft happens in many different ways, from internal actors stealing the physical copies left on the printer to botnets that extract data stored on the hard drive. When a company experiences the unauthorized movement of data via malware, it’s known as exfiltration or data extrusion.
Unsecured printers (or other pieces of office equipment) are vulnerable to these attacks that can lead to sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking occurs when malware installs illicit software on a device to harness processing power for mining cryptocurrencies. Often, such malware positions itself on a router or other device with direct access to multiple computers to maximize available power.
Without the proper security measures in place, printers can be taken over in this capacity, which often results in disrupted workflows and machine downtime.
Email attacks
Researchers found that a number of printer models had a flaw that allowed email hacking.
“[HP] announced that more than 200 printer models are impacted by a severe remote code execution vulnerability that was exploited by researchers at the Pwn2Own hacking contest last year, where participants earned a total of more than $1 million.”
In short, these vulnerabilities are considered to be significant and can be exploited to execute code remotely, siphon data and sensitive information, or even launch a denial of service (DoS) attack.
Hacking
Any network-connected device is susceptible to being hacked, whether it’s a smartphone, a laptop, or even a smart thermostat. Hackers can infiltrate a network through printers, access unsecured data on the hard drive, and jump to other parts of the company’s network to wreak even more havoc.
While there is no ultimate solution that prevents 100% of hack attempts, the more robust your security strategy is, the better your chances at being left alone are, as threat actors go after the easiest targets available.
Printer Tampering
Unsecure printer settings can be altered—intentionally or accidentally—to reduce document security. Changes might include saving jobs to another area, rerouting jobs entirely, or resetting the device to its factory settings to eliminate any custom security features which may have been installed.
To combat these types of attacks, your company should create access controls around factory resets, and other security settings that could influence the overall risk levels of your office equipment.
Cyber Hygiene, User Awareness, and Printer Security
Printers are often an overlooked aspect of cyber hygiene even though large profile cyber incidents continue to demonstrate how printers and other endpoints, if left unsecured, cause major security risks and make easy targets for threat actors. Therefore, businesses must take steps to secure their printers to maintain a clean, secure document environment.
By implementing printer security best practices, organizations can reduce the cyber risk that office equipment and other network enabled devices bring to the table without disrupting workflows or interrupting existing processes.
Best Practices for Printer Security
To amplify your printer security, adhere to the following best practices that minimize the risk associated with network-enabled office equipment:
- Leverage integration software to ensure a holistically secure print environment. Encourage users to adopt the native software provided by network-connected devices, such as Konica Minolta’s AccurioPro Connect. Printer manufacturers designed these tools to improve printer security without sacrificing the workflow enhancements their products deliver to an office.
- Secure the printer at its source. Require users to identify and authenticate themselves before they’re able to use the printing functions. This protects access to sensitive information and helps spot unauthorized access.
- Encrypt all print jobs while in transit. Encrypting the print jobs that are released to the printer prevents digital interception or document theft from the printer’s hard drive.
- Configure the printer so it doesn’t store the office’s print history. Print jobs stored on the hard drive constitute a goldmine for cybercriminals. Eliminating it makes the printer less enticing.
- Develop a formal policy against abandoned printouts. Remind users that security extends beyond the digital environment into the physical realm. Train users on print reduction tactics, and to only print what they need.
The Role of Managed Print Services
As the business world continues to firmly rely on printing, many businesses choose to address these functions by entering a strategic partnership with a managed print service provider.
Whereas office equipment and cybersecurity represent major investments for any company, managed print services introduce the necessary skills and experience organizations typically lack. By doing so, these companies gain advantages which nurture growth without the need to staff full internal teams.
An MPS provider helps:
- Improve operational efficiency beyond what the company might have been able to develop on their own.
- Access technological upgrades previously out of reach.
- Take advantage of more sophisticated tools such as mobile printing, cloud-based document processes, and automation for your business.
- Reduce overall security risks.
- Focus on initiatives which directly contribute to the growth of your company.
Today’s cybercriminals are as tenacious as customers are unforgiving. There’s no room for complacency or missteps, which makes a strategic partnership with a managed service provider an excellent solution for organizations looking to fill their knowledge and capability gaps.
Printer Security Key Takeaways
Many businesses overlook printer security even though this equipment contains hard drives, firmware, and a CPU—the basic components of a computer. As part of the infrastructure through which documents and data flow, printers represent a critical endpoint which requires robust security measures be put in place.
Engaging in print security best practices will help you protect your network while also furthering the development of a culture of security awareness.
Subscribe to the Impact blog for regular updates on business technology solutions, industry trends, and how modern organizations are addressing the growing need for robust cybersecurity strategies.